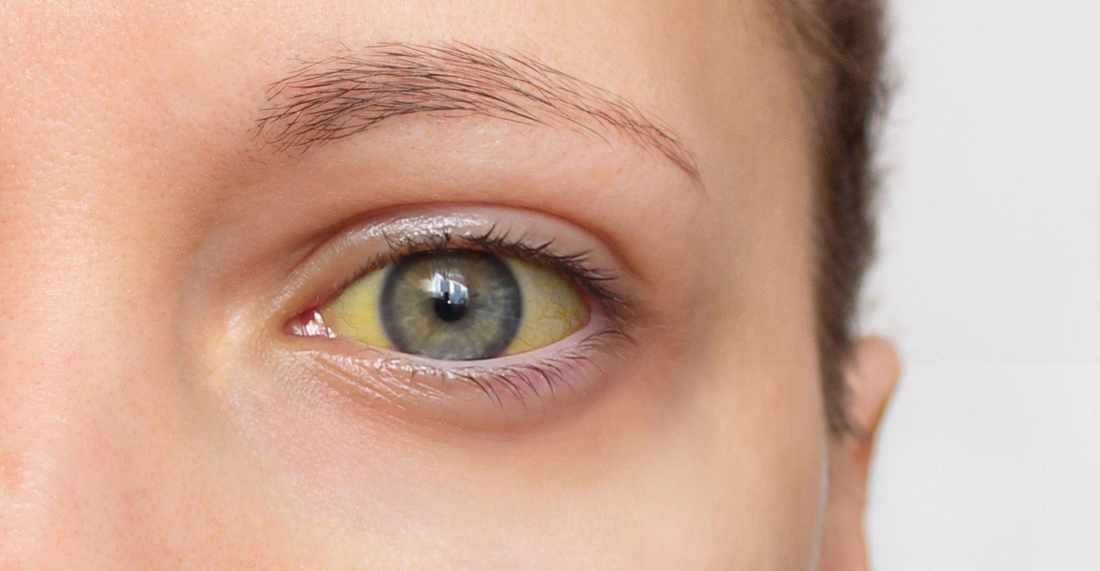

Jaundice is a condition that causes yellowing of the skin and eyes due to excess bilirubin in the blood. It can affect newborns, adults, and the elderly, often signalling an underlying liver issue or infection. Proper care for a jaundice patient involves recognising early symptoms, following a liver-friendly diet, and making necessary lifestyle adjustments to aid recovery.
Understanding the treatment of jaundice in adults, when to worry about jaundice in adults, and the signs of recovery from jaundice in newborns is crucial for effective management. This guide covers all you need to know to care for a jaundice patient and help them recover smoothly.
Jaundice is a condition that causes yellowing of the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes due to excess bilirubin in the blood. Bilirubin is a yellow pigment produced when red blood cells break down. Normally, the liver processes bilirubin and excretes it through bile. However, when this process is disrupted, bilirubin builds up, leading to jaundice.
Bilirubin, a byproduct of red blood cell breakdown, is usually processed by the liver. Disruptions in this process can result in jaundice. Let’s see what can cause this disruption:
Liver inflammation, scarring, excess fat, and tumours in the liver can all impair bilirubin processing and cause jaundice.
Gallstones, tumours or cysts, and inflammation or infections can block bile flow in the liver, pancreas, or bile ducts.
Haemolytic anaemia is when red cells break down quickly, causing excess bilirubin. Genetic disorders like Sickle Cell Disease and Thalassaemia, as well as infections like Malaria and Sepsis, can also lead to rapid red cell destruction.
Gilbert’s Syndrome causes occasional jaundice due to bilirubin metabolism issues, while Crigler-Najjar Syndrome is a rare disorder that makes it difficult for the body to process bilirubin.
Excessive alcohol consumption, certain medications, and poisoning from hepatotoxic substances can damage liver cells, impair liver function, and lead to jaundice.
Recognising the early symptoms of jaundice in adults is essential for timely intervention. These include:
If jaundice is accompanied by severe pain, fever, or confusion, immediate medical attention is required. Early diagnosis and treatment of the underlying cause can help manage jaundice effectively.
Mild cases of jaundice may not be serious, but persistent or worsening jaundice could indicate a severe health issue that requires medical attention.
So what should you do if you notice such symptoms on a loved one?
The treatment of jaundice in adults depends on the underlying cause. Since jaundice itself is a symptom rather than a disease, addressing the root problem is crucial for recovery.
If the root cause of jaundice is liver disease then the following lines of treatment are commonly followed:
Jaundice can be caused by bile duct obstruction, which usually happens in two ways.
In case excessive red blood cell breakdown is the root cause, it may be caused by two conditions:
No matter what the root cause is, all jaundice patients require supportive care which includes:
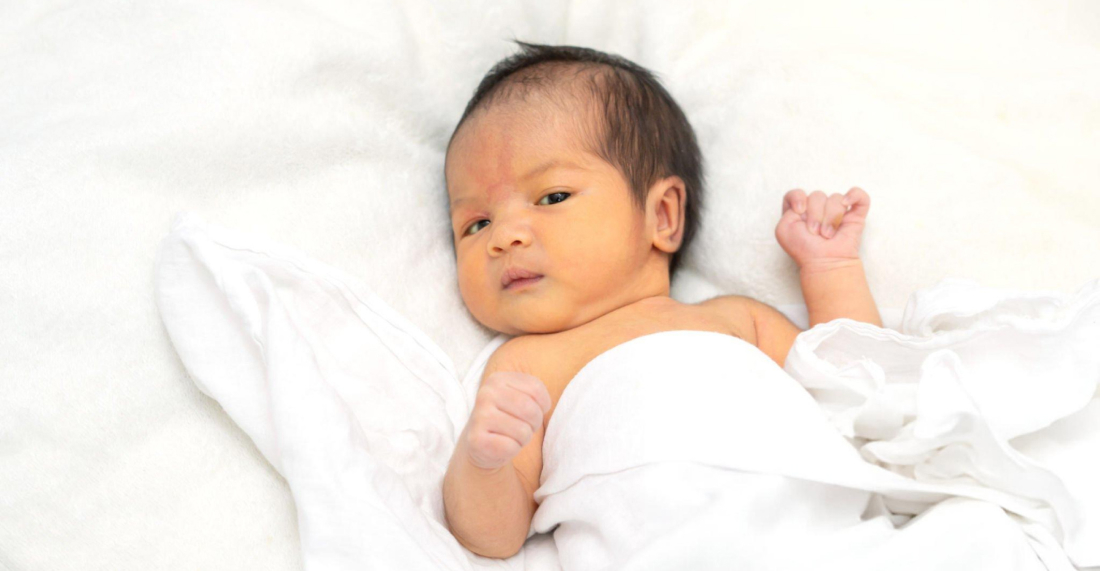

Neonatal jaundice is common, usually appearing within 2-4 days of birth. While it often resolves naturally, signs of recovery from jaundice in newborns are important to track.
Treating newborns with jaundice, of course, requires a more delicate approach. It usually involves:
Most cases of newborn jaundice resolve within 1-2 weeks without complications. However, parents should monitor symptoms and seek medical care if jaundice worsens to prevent complications such as kernicterus, a rare but serious brain damage caused by high bilirubin levels.
A well-balanced diet plays a crucial role in supporting liver function and aiding recovery from jaundice. Since jaundice is often linked to liver dysfunction, consuming the right foods can help detoxify the liver, improve digestion, and promote overall well-being.
To improve digestion, consuming small, frequent meals throughout the day is recommended. Avoiding late-night eating can help reduce strain on the liver. Additionally, ensuring you get enough rest and effectively managing stress are crucial factors that can impact the health of your liver.
Recovering from jaundice involves not only medical treatment but also lifestyle changes to support liver function and overall health. Healthy habits can help speed up recovery and prevent future liver problems, as the liver is crucial for detoxifying the body.
Drink plenty of water daily, aiming for at least 8-10 glasses, to effectively flush out toxins from your body. Opt for hydrating fluids such as coconut water, fresh fruit juices, and herbal teas to keep your body well-hydrated. Sugary and carbonated drinks should be avoided as they can put a strain on the liver.
Incorporate fresh fruits and vegetables such as carrots, beets, apples, and leafy greens into your diet. Opt for whole grains like brown rice and oats instead of refined grains. Incorporate lean proteins such as lentils, fish, and tofu while steering clear of red meat. Avoid fried, processed, and high-fat foods as they can impede liver recovery.
Ensure you get a minimum of 7-9 hours of sleep each night to facilitate the body’s healing process. It is important to minimise stress and incorporate relaxation techniques such as meditation or deep breathing into your daily routine.
Alcohol is known to directly harm the liver and impede the body’s ability to recover, so it is best to avoid it altogether. Smoking introduces harmful toxins into the body, which can further strain the liver. It is advisable to refrain from smoking as well to support liver health and overall well-being.
Once you start feeling better, consider incorporating gentle physical activities such as walking or yoga into your routine. Avoid engaging in strenuous exercise during the recovery period, as it can potentially exhaust the body.
Follow your doctor’s instructions and take your prescribed medications as directed. Additionally, schedule regular liver function tests to track your progress in recovery.
Wash your hands before eating to prevent infections. Additionally, avoid sharing personal items to reduce the risk of spreading hepatitis-related jaundice.
Caring for a jaundice patient requires a holistic approach that includes proper medical attention, a liver-friendly diet, and a healthy lifestyle. Recognising symptoms early – such as yellowing of the skin and eyes, fatigue, and digestive issues – can help in timely diagnosis and treatment.
A well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and adequate hydration plays a crucial role in supporting liver function and speeding up recovery. Additionally, lifestyle modifications like getting enough rest, avoiding alcohol, and managing stress can prevent further complications and promote overall well-being.
To care for a jaundice patient, ensure proper hydration, a liver-friendly diet, adequate rest, and timely medical attention while avoiding alcohol and fatty foods.
Avoid fatty, fried, processed foods, red meat, alcohol, sugary drinks, and high-sodium foods to prevent liver strain during jaundice recovery.
Sources:
Spread the love, follow us on our social media channels