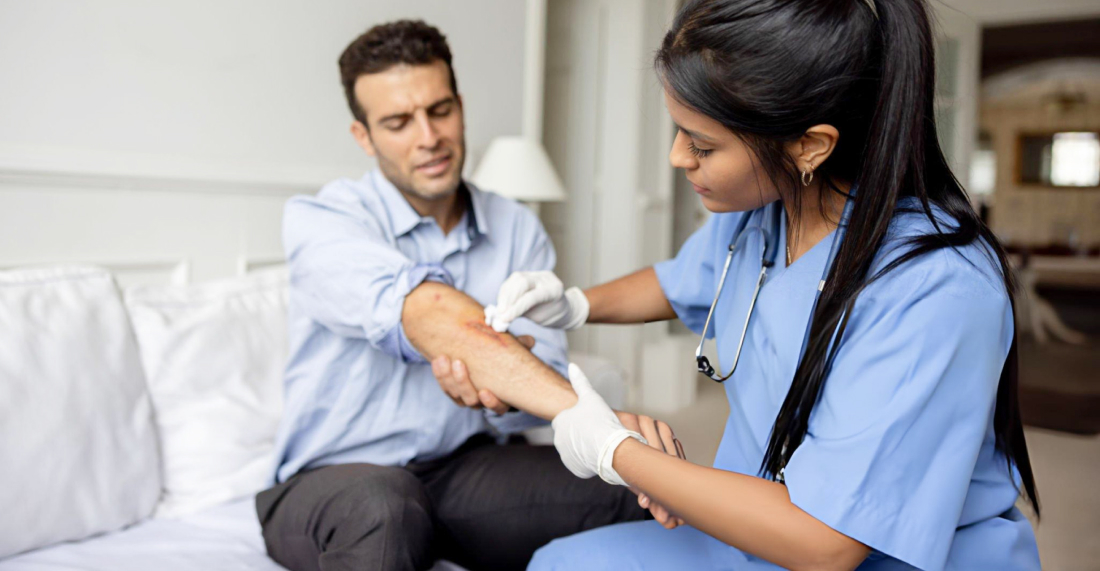

Wound care is important for promoting healing and preventing infection. It goes beyond basic first aid and includes specialised medical treatment. Understanding different types of wounds and proper wound management is important for faster healing and minimising scarring.
This guide will cover the fundamentals of wound care, discuss various wound types, and offer expert tips for optimal healing.
A wound is any disruption to the skin and underlying tissues caused by injury, surgery, burns, or medical conditions. The body naturally works to repair wounds through a multi-stage healing process.
A wound heals in four stages:
There are several approaches to wound care, depending on the severity and nature of the wound. Let’s look at the most common types of wound care:
For small cuts, scrapes, and abrasions, basic first aid is usually sufficient. The steps include:
Post-surgical wounds require careful attention to prevent complications. This includes:
Chronic wounds, such as diabetic ulcers and pressure sores, require specialised care. They often take longer to heal and need:
Burn wounds vary in severity and require different treatment approaches:
For severe wounds, medical professionals may use advanced treatments, such as:
Managing wound care at home is important for preventing complications. Here are some best practices:
Clean wounds daily with saline solution or mild soap and water to remove bacteria and debris.
Different wounds require different dressings. Some common options include:
Look out for:
Proper nutrition supports wound healing. Include:
For pressure ulcers or diabetic wounds, frequent repositioning and the use of supportive cushions can prevent worsening.
Scabs protect wounds during healing. Picking at them can delay recovery and increase scarring.
If you have a complex wound (surgical, deep cuts, or ulcers), follow your doctor’s instructions for wound care nursing and treatment.
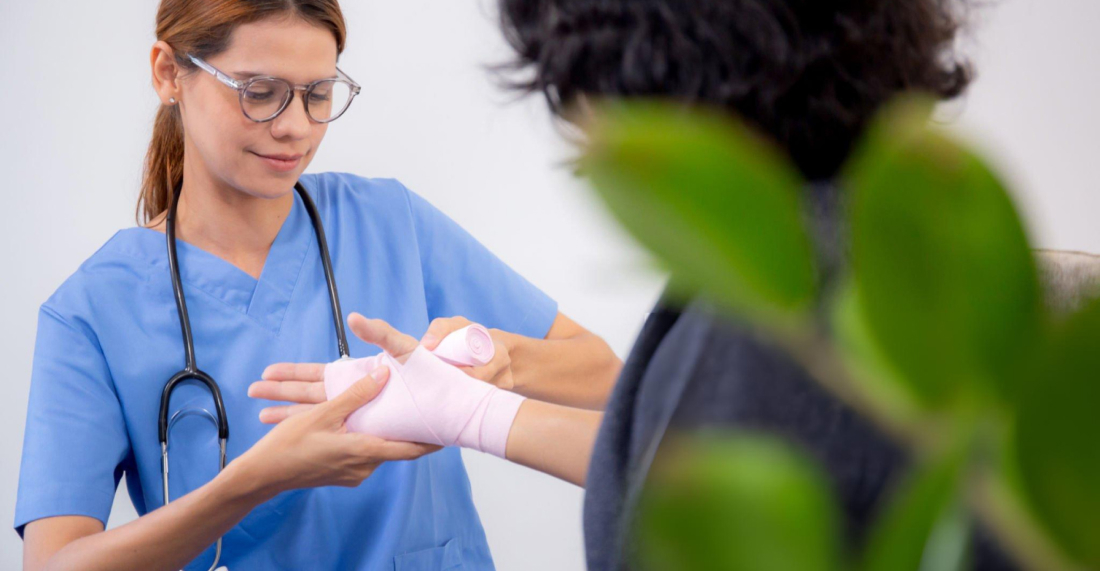

Wound care nursing is a specialised field focused on helping patients recover from acute and chronic wounds. These nurses are trained to:
Wound care nurses play an important role in hospitals, nursing homes, and home healthcare settings. Their expertise helps prevent complications, especially in patients with diabetes, bed sores, or post-surgical wounds.
While wound care is essential, prevention is always better than treatment. Here are ways to minimize the risk of wounds:
Wound care extends beyond just applying a bandage. Whether you’re handling wound care at home or working in wound care nursing, understanding the right treatments can make a huge difference in healing outcomes. From minor scrapes to chronic ulcers, proper wound management ensures faster recovery, prevents infections, and improves overall well-being.
If you have a wound that won’t heal, it’s important to see a doctor for proper treatment. With the right care, even small or large wounds have the potential to heal and strengthen the body.
Sources:
Spread the love, follow us on our social media channels