

Stroke is a significant health issue that affects millions globally, and Malaysia is no exception. It is one of the leading causes of disability and death in the country, impacting not only the individual who suffers but also their families.
Let’s understand more about stroke in this article.
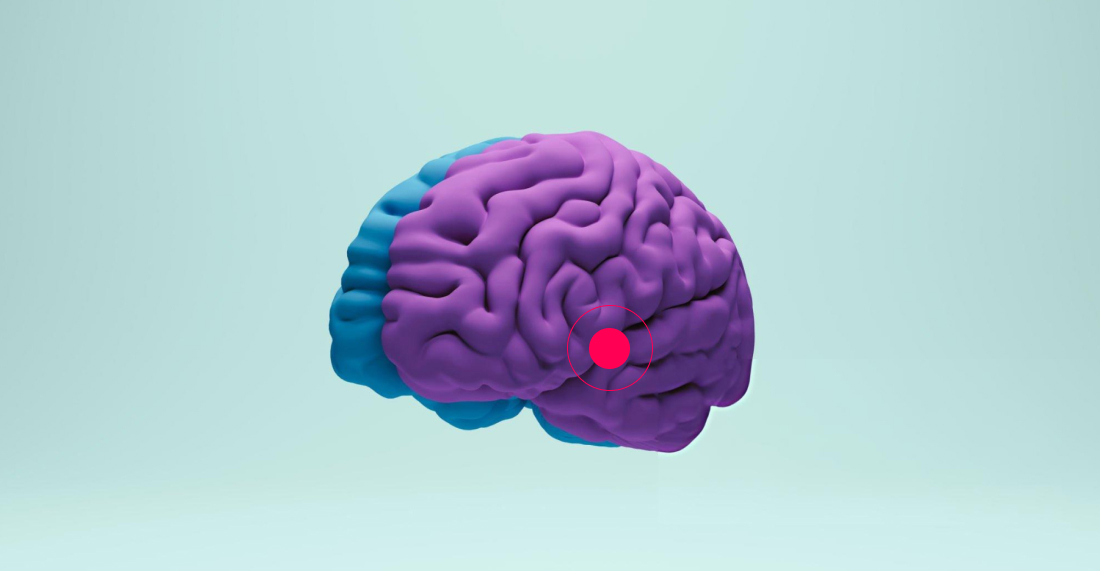
A stroke occurs when the blood supply to a part of the brain is disrupted, either due to a blockage or a rupture in a blood vessel. This interruption deprives brain cells of oxygen and nutrients, causing them to die within minutes. Prompt treatment plays a vital role in minimising brain damage and improving outcomes.
There are three primary types of strokes, with each type has distinct characteristics, causes, and implications for the patient.
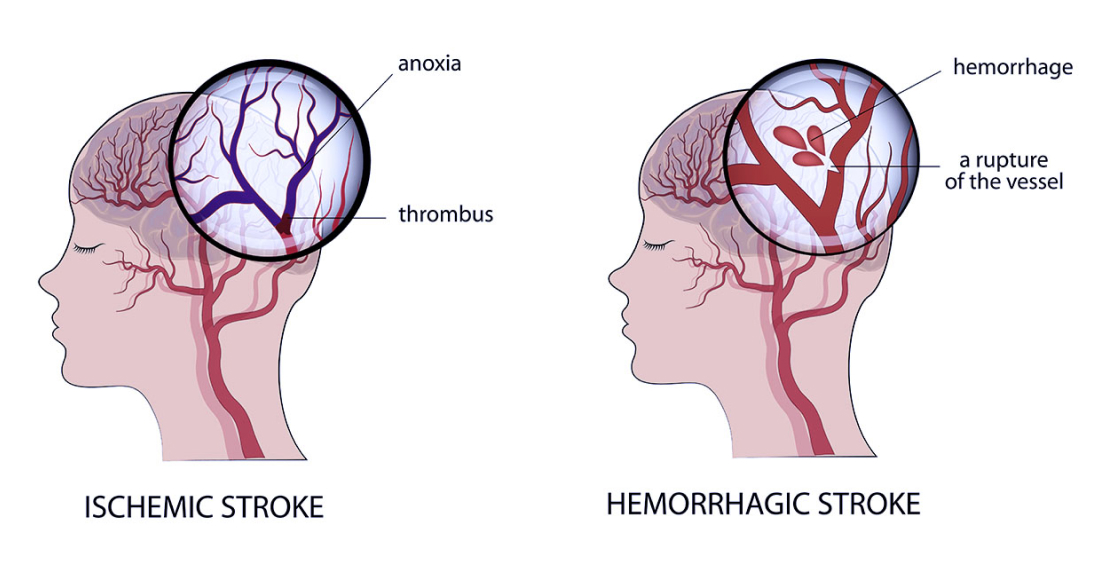
Ischemic stroke is the most common type of stroke, making up 87% of cases globally. It happens when a clot blocks blood flow to the brain, leading to a lack of oxygen and nutrients. This blockage is often due to fatty deposits in the blood vessels or clots from other parts of the body. Treatment involves quickly dissolving or removing the clot using medications like tPA or mechanical thrombectomy.
Haemorrhagic stroke is caused by a burst blood vessel in the brain, leading to bleeding and pressure that harms nearby brain tissue. It can be due to conditions like high blood pressure, aneurysms, or trauma. There are two types of haemorrhagic stroke: bleeding within the brain tissue or bleeding in the space around the brain. Treatment typically involves stopping the bleeding, reducing pressure, and repairing the damaged vessel with surgery or other procedures.
A transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a temporary blockage of blood flow to the brain, resembling a stroke but with symptoms that resolve within 24 hours and no permanent damage. It is a warning sign of a potential major stroke and requires immediate medical attention to address underlying risk factors and prevent future strokes.
The prevalence of stroke in Malaysia is affected by numerous common causes and risk factors such as:
Women have unique risk factors that make them more susceptible to stroke. In Malaysia, stroke among women is becoming increasingly prevalent due to the following causes:
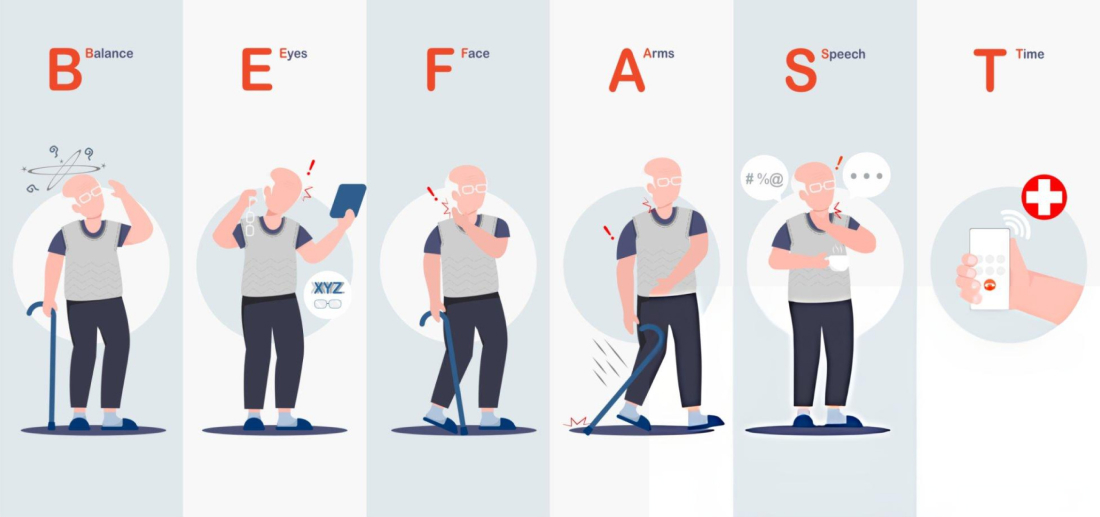
Recognising the signs and symptoms of a stroke early can save lives and reduce the potential for long-term damage. The most common symptoms to watch for are:
Seeking immediate medical attention during a stroke is crucial to minimise brain damage and improve recovery outcomes. The first few hours after a stroke are crucial, as brain cells begin to die without oxygen and nutrients. Timely treatment, such as clot-busting medications or procedures to remove blockages, can significantly improve chances of recovery and prevent complications like permanent disability or cognitive impairment. Recognising stroke symptoms and seeking emergency care promptly is essential.
The treatment for a stroke depends on the type of stroke (ischemic or haemorrhagic) and how quickly medical care is received. The main goal is to restore blood flow to the brain and prevent further damage. Here are the primary treatment options:
The most common treatment for ischemic stroke is the administration of tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), which can dissolve the clot and restore blood flow if given within 3 to 4.5 hours of the stroke’s onset.
If tPA is not an option or if the clot is too large, doctors may perform procedures such as mechanical thrombectomy, where a catheter is used to remove the clot directly. To prevent further clotting, patients may be prescribed aspirin or other blood thinners.
If there is a brain haemorrhage, surgery may be required to repair the blood vessel, remove the blood clot, or relieve pressure on the brain. In some cases, the surgeon may need to remove blood that has pooled in the brain to prevent further damage.
To control bleeding and lower blood pressure, medications may be given to prevent further bleeding or to reduce the pressure on the brain.
Recovery after a stroke is crucial for patients to regain independence and improve their quality of life. The rehabilitation plan, tailored to the severity of the stroke, affected brain areas, and overall health, usually includes physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and psychological support.

Preventing a stroke is often possible by addressing key risk factors and adopting a healthy lifestyle. Here are some important preventive measures to reduce the risk of strokes:
Stroke is a life-altering event that can be devastating for individuals and their families. By understanding the stroke meaning, types of strokes, stroke causes, and treatment options, families in Malaysia can take proactive steps to prevent and manage this condition. Early intervention and lifestyle changes are key to improving outcomes and reducing the impact of stroke on families.
Through education and awareness, we can work together to combat the rising prevalence of stroke and create a healthier future for all Malaysians.
A stroke is caused by a disruption in the blood supply to the brain, either due to a blockage (ischemic) or bleeding (haemorrhagic).
A stroke is a medical condition where blood flow to the brain is interrupted, causing brain cells to be damaged or die.
Stroke can be prevented by managing risk factors like high blood pressure, cholesterol, diabetes, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol.
Stroke treatment involves seeking immediate medical attention to restore blood flow, manage symptoms, and begin rehabilitation for recovery.
Sources:
Spread the love, follow us on our social media channels